
Aquifers are sub-surface groundwater areas used to model the vertical movement of water infiltrating from the subcatchments that lie above them. They also permit the infiltration of groundwater into the drainage system, or exfiltration of surface water from the drainage system, depending on the hydraulic gradient that exists. The same aquifer object can be shared by several subcatchments. Aquifers are only required in models that need to explicitly account for the exchange of groundwater with the drainage system, or to establish base flow and recession curves in natural channels and non-urban systems.
Aquifers are represented using two zones - an un-saturated zone and a saturated zone.
Their behaviour is characterised using parameters such as soil porosity, hydraulic conductivity, evapotranspiration depth, bottom elevation, and loss rate to deep groundwater. In addition, the initial water table elevation and initial moisture content of the unsaturated zone must be supplied.
Aquifers are connected to subcatchments and to drainage system nodes as defined in a subcatchment's Groundwater Flow property. This property also contains parameters that govern the rate of groundwater flow between the aquifer's saturated zone and the drainage system node.
|
Option
|
Description |
|
Aquifer Selector |
Select the aquifer to edit. |
|
Add |
Click to add a new aquifer to the project. |
|
Delete |
Click to delete an aquifer from the project. |
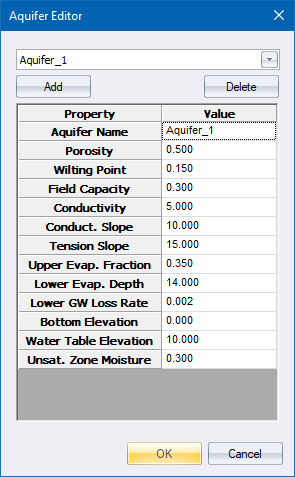
The table allows you to specify the following data for the aquifer.
|
Option
|
Description |
|
Aquifer Name |
User-assigned aquifer name. |
|
Porosity |
Volume of voids/total soil volume (volumetric fraction). |
|
Wilting Point |
Soil moisture content at which plants cannot survive (volumetric fraction). |
|
Field Capacity |
Soil moisture content after all free water has drained off (volumetric fraction). |
|
Conductivity |
Soil's saturated hydraulic conductivity (mm/hr or in/hr ). |
|
Conductivity Slope |
Average slope of conductivity versus soil moisture content curve (mm/hr or in/hr). |
|
Tension Slope |
Average slope of soil tension versus soil moisture content curve (mm or inches). |
|
Upper Evaporation Fraction |
Fraction of total evaporation available for evapotranspiration in the upper unsaturated zone. |
|
Lower Evaporation Depth |
Maximum depth into the lower saturated zone over which evapotranspiration can occur (m or ft). |
|
Lower Groundwater Loss Rate |
Rate of percolation from saturated zone to deep groundwater (mm/hr or in/hr). |
|
Bottom Elevation |
Elevation of the bottom of the aquifer (m or ft). |
|
Water Table Elevation |
Elevation of the water table in the aquifer at the start of the simulation (m or ft). |
|
Unsaturated Zone Moisture |
Moisture content of the unsaturated upper zone of the aquifer at the start of the simulation (volumetric fraction). This cannot exceed soil porosity. |
See Also Groundwater Flow Editor, Edit Aquifers.